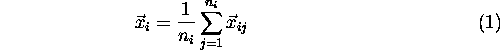
where
Creation of the mesh can be tedious work if no automated algorithm is available. Most geometry can be converted semi-automatic. At boundaries and element connections some anomalies may occur. Anomalies are hard to solve manually. After initial mesh generation smoothing can be considered as a way to improve overall mesh at preprocessing stage. The type of input geometry and type of analysis normally dictates meshing algorithm. Several initial node placement algorithms can be used for structured or unstructured mesh configuration. For triangular and tetrahedral meshes random node placement can also be used.
Simple smoothing technique is Laplacian
smoothing[2, 3]. For each point is moved to
barycentre of the neighboring points. New position for each point can
be calculated as
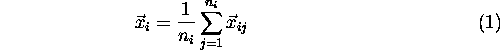
where ![]() are
are ![]() total nodes connected to point i. The
process converge in 2 to 5 iterations. Problems can occur when
boundaries are not convex. Then some points can be smoothed out of the
region. Only minor irregularities in mesh can be corrected with such
method. Also it is difficult to retain initial node spacing when
using Laplacian smoothing. Smoothing with physically based connections
between nodes can be successful approach. Shimada[7]
has shown that Non-Manifold mesh generation can be fully automated for
triangles and tetrahedra.
total nodes connected to point i. The
process converge in 2 to 5 iterations. Problems can occur when
boundaries are not convex. Then some points can be smoothed out of the
region. Only minor irregularities in mesh can be corrected with such
method. Also it is difficult to retain initial node spacing when
using Laplacian smoothing. Smoothing with physically based connections
between nodes can be successful approach. Shimada[7]
has shown that Non-Manifold mesh generation can be fully automated for
triangles and tetrahedra.